Heading Title
Hey Family,
It’s Crystal checking in, hope everyone is having a fantastic week. Just sending a friendly reminder that our shop is open for business. Check out the deets below!!
wetakeoncancer.com/shop
Happy Shopping,
Crystal Jordan, founder of WE Take On Cancer
Former Teen Summit Host, Ananda Lewis Shares Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Photo: ImAnandalewis Instagram
If you grew up in the 90’s and kept your television on BET like me, then you’re probably familiar with the hit show “Teen Summit” that dealt with everyday issues surrounding teenagers. One of the former host, Ananda Lewis, now 47 announced Thursday (Oct 1st) the beginning of Breast Cancer Awareness month of her almost two year battle with stage 3 breast cancer in her lymph nodes on her Instagram page. In her emotional video she regrets not taking mammograms seriously due to her own mother being diagnosed in the past after having mammograms for nearly 30 years and exposure to radiation.
As a cancer research professional, I know cancer does not discriminate; so to learn of her diagnosis still comes as a shock.
“If I had done the mammograms from the time they were recommended, when I turned 40, they would have caught the tumor in my breast years before I caught it through my own breast exam, self exam and thermography,” Lewis said. “And they would have caught it at a place where it was more manageable. Where the treatment of it would have been a little easier. It’s never easier, but I use that word in comparison to what I’m going through now. Instead, what I’m dealing with is stage 3 breast cancer that is in my lymphs. I need you to get your mammograms.”
In 2020 alone, the NBCF reports “an estimated 276,480 new cases of invasive breast cancer will be diagnosed in women in the U.S. as well as 48,530 new cases of non-invasive (in situ) breast cancer,” adding that an estimated 42,170 women will die of the disease this year. For Black women, the risk is especially high; though comprising just under 14 percent of the total female population (h/t Catalyst, Inc.) the Susan G. Komen Foundation reports that Black women nearly equal white women in the highest rate of breast cancer occurrences, with a 12 percent likelihood of diagnosis in their lifetimes. Black women under 40 also have higher rates of breast cancer compared to white women, and at every age, are most likely to be diagnosed with more aggressive triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC), which spread more quickly to lymph nodes (which can distribute cancel cells throughout the body) and are more difficult to survive.
It’s very important to take advantage of early detection, do your self-checks in the shower, the couch, bed or wherever you feel comfortable and please inquire about mammograms with your primary care physician. Matter of fact, I got my reminder letter in the mail recently to schedule my appointment. I’m not 40, but I have a family history of breast cancer.
With Ananda sharing her story with the world, I hope this will convince both men & women, yes men (ya’ll get it too!) to check your boobs.
Thank you for sharing your truth, Ananda and WE are sending you GOOD energy!!
MAGGIE FOX, NBC News
There’s not enough evidence to say whether coffee might cause cancer or protect against it, a global body of cancer experts said Wednesday.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) stepped down its classification of coffee as a possible cause of cancer, and says its fresh review of the evidence shows it’s not clear whether it does or not.
But very, very hot drinks might, the IARC, part of the World Health Organization, said.
“Coffee is not classifiable as to carcinogenicity,” said Dana Loomis, an expert on disease patterns at the University of Nebraska Medical Center who led the study committee.
The team went through more than 1,000 studies done from the 1970s to this year and could reach no conclusion “either that it is safe or that it is dangerous,” Loomis told reporters on a telephone briefing.
But there’s good news for women.
“More than 40 cohort and case-control studies and a meta-analysis including nearly 1 million women consistently indicated either no association or a modest inverse association for cancer of the female breast and coffee drinking,” the team wrote.
It’s the first time IARC has looked at coffee since it said in 1991 that coffee was a possible cause of cancer, based on some studies linking coffee drinking with bladder cancer. “The Working Group concluded that positive associations reported in some studies could have been due to inadequate control for tobacco smoking, which can be strongly associated with heavy coffee drinking,” IARC said in a statement.
“The current evaluation is based on a much larger and stronger body of evidence.”
However, evidence from groups, mostly in South America where a very hot mate is consumed, showed that extremely hot drinks — 150 degrees F or hotter — just might be linked with cancer, the group said.
“The Working Group noted that the epidemiological evidence for very hot beverages and human cancer has strengthened over time,” it said.
Extremely hot drinks might damage the cells in the esophagus enough to sometimes cause cancer, the group said.
IARC issues very broad classifications of definite, probable and possible cancer-causing agents. Their reports don’t say how much something might raise the risk of cancer, so unless they are read carefully, it can be easy to confuse a very high risk — such as smoking — with a very low risk.
The team doesn’t do direct research but reviews the quality and quantity of existing evidence. The classifications are not necessarily meant for the general public but are meant to guide policymakers.
Inflammation is a normal physiological response that causes injured tissue to heal. An inflammatory process starts when chemicals are released by the damaged tissue. In response, white blood cells make substances that cause cells to divide and grow to rebuild tissue to help repair the injury. Once the wound is healed, the inflammatory process ends.
In chronic inflammation, the inflammatory process may begin even if there is no injury, and it does not end when it should. Why the inflammation continues is not always known. Chronic inflammation may be caused by infections that don’t go away, abnormal immune reactions to normal tissues, or conditions such as obesity. Over time, chronic inflammation can cause DNA damage and lead to cancer. For example, people with chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, have an increased risk of colon cancer.
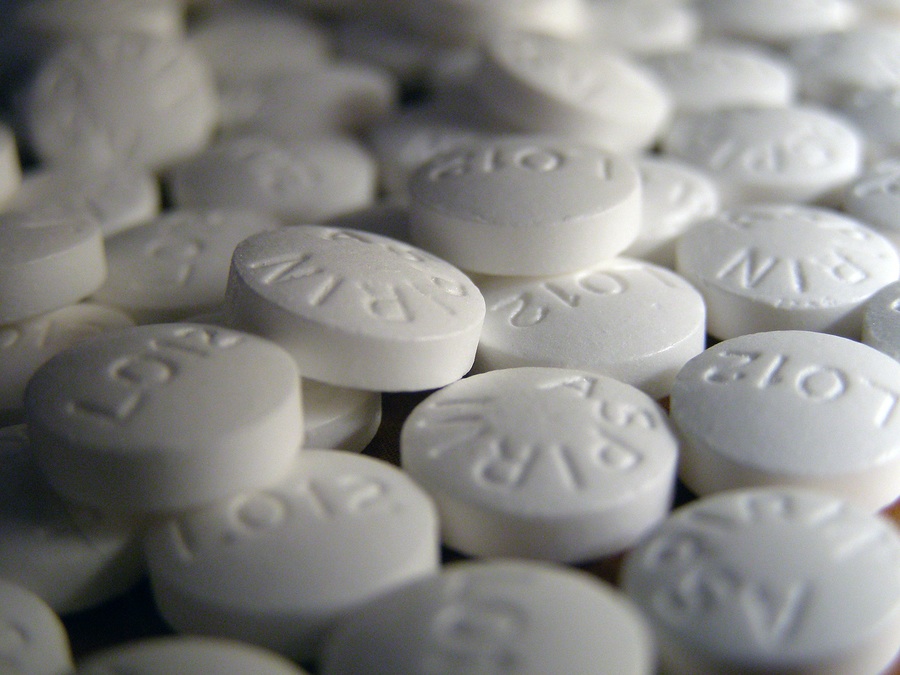
Many studies have investigated whether anti-inflammatory medications, such as aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, reduce the risk of cancer. However, a clear answer is not yet available. For more information, see No Easy Answers about Whether Aspirin Lowers Cancer Risk.
This article was originally published on cancer.gov.
Photo:IStock
Broccoli — and to an even greater degree broccoli sprouts — has gained a reputation as a potent cancer-fighter, and recent research sheds new light on the actual mechanics behind its chemoprotective abilities.
One of the compounds in broccoli known to have anti-cancer activity is sulforaphane, a naturally occurring organic sulfur.
Studies have shown sulforaphane supports normal cell function and division while causing apoptosis (programmed cell death) in colon, prostate, breast and tobacco-induced lung cancer4 cells, and reducing the number of cancerous liver tumors in mice.5
Three servings of broccoli per week may reduce your risk of prostate cancer by more than 60 percent. Now, Oregon State University (OSU) researchers believe they’ve discovered yet another way sulforaphane works to protect you against cancer.
How Sulforaphane Prevents Cancer From Spreading
More than 90 percent of the DNA sequences in your genome are thought of as “junk DNA,” having no perceptible function as they do not code for proteins. Alas, mounting research is now revealing the fallacy of such thinking. As suspected, nature does not waste material, nor does it create useless junk.
As noted in a recent paper discussing micro RNA (miRNA) and long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) interactions in the circulatory system, advances in DNA analysis have revealed that as much as 98 percent of the human genome encodes for noncoding transcripts.
Common sense would suggest 98 percent of the human genome could not be purposeless “junk” as previously thought.
It turns out differences between higher and lower organisms may actually arise from differences in these noncoding transcripts more so than the actual genetic code of any given organism. The paper goes on to explain:
“Many of these noncoding transcripts are processed to generate small noncoding RNA such as miRNA, or lncRNA. Through their interaction with DNA, RNA and proteins noncoding RNA have emerged as key regulators of gene expression under both physiological and pathological conditions …
Interestingly, cross-regulatory networks between miRNAs and lncRNA have recently been identified. A number of detailed sequencing studies have revealed that lncRNA are preferentially expressed in a tissue‐specific manner, suggesting that they hold great promise as selective targets in disease.”
Getting back to broccoli, scientists at OSU discovered that sulforaphane significantly reduces the expression of lncRNAs in prostate cancer cells, thereby influencing the miRNA and reducing the cancer cells’ ability to form colonies by as much as 400 percent.
So much for junk DNA! Lead OSU investigator Emily Ho, Ph.D., commented on her team’s findings, saying:
“It’s obviously of interest that this dietary compound, found at some of its highest levels in broccoli, can affect lncRNAs. This could open the door to a whole range of new dietary strategies, foods or drugs that might play a role in cancer suppression or therapeutic control.”
Sulforaphane Combats Cancer in More Ways Than One
Sulforaphane also reduces damaging reactive oxygen species (ROS) by as much as 73 percent, thereby lowering your risk of inflammation— another hallmark of cancer. It’s also an immune stimulant,14 and having robust immune function is your first line of defense against not only cancer but all disease.
Sulfur-rich cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli also play an important role in detoxification, which is yet another factor that can affect your cancer risk. Broccoli sprouts, in particular, have been shown to help detox environmental pollutants such as benzene. As noted by The World’s Healthiest Foods:
“… [S]ulforaphane increases the activity of the liver’s phase 2 detoxification enzymes. These enzymes … are well known for their ability to clear a wide variety of toxic compounds from the body including not only many carcinogens, but also many reactive oxygen species, a particularly nasty type of free radical.
By jump starting these important detoxification enzymes, compounds in crucifers provide protection against cell mutations, cancer and numerous other harmful effects that would otherwise be caused by these toxins.”
Other Anti-Cancer Compounds in Broccoli
Aside from sulforaphane, broccoli contains several other health-promoting, chemoprotective nutrients and compounds, including:
• Fiber, which helps nourish your gut microbiome to strengthen your immune function and reduce your risk of inflammatory diseases. Fiber also activates a gene called T-bet, which is essential for producing immune cells in the lining of your digestive tract.20
These immune cells, called innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), help maintain balance between immunity and inflammation in your body and produce interleukin-22 (IL-22), a hormone that helps protect your body from pathogenic bacteria.
ILCs even help resolve cancerous lesions and prevent the development of bowel cancers and other inflammatory diseases.
• Glucoraphanin, a glucosinolate precursor of sulforaphane that influences carcinogenesis and mutagenesis. Compared to mature broccoli, broccoli sprouts can contain up to 20 times more glucoraphanin.
• Phenolic compounds, including flavonoids and phenolic acids, which have a potent ability to eliminate damaging free radicals and quell inflammation, resulting in a lower risk for diseases such as asthma, type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
One of the ways phenolic compounds slow the encroachment of disease is by defending against infection, most dramatically by zapping ROS linked to atherosclerosis and neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
• Diindolylmethane (DIM). Your body produces DIM when it breaks down cruciferous vegetables. Like many other broccoli compounds, DIM has shown multiple potential benefits, including boosting your immune system and helping to prevent or treat cancer.
• Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), an enzyme involved in the production of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), a compound involved in mitochondrial health and energy metabolism. NAD may slow age-related decline in health by restoring your metabolism to more youthful levels.
Previous research has shown that, with age, your body loses its capacity to create NAD — an effect thought to be related to, or the result of, chronic inflammation. Studies have also shown that taking NAD directly is ineffective. Instead, you’re better off taking its precursor, NMN, found in broccoli, cucumbers, cabbage, avocado and other green vegetables. Once in your system, NMN is quickly converted into NAD.
Broccoli Reduces Risk of Fatty Liver and Liver Cancer
Broccoli may also be an important dietary intervention for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which affects up to 25 percent of Americans, including children. NAFLD is defined as an excessive accumulation of fats in your liver in the absence of significant alcohol consumption.
The overconsumption of net carbs, especially fructose from processed foods, soda and juices, is strongly associated with NAFLD which, if left untreated, can raise your risk of liver cancer.
Recent research suggests the fat-forming and pro-inflammatory effects of fructose may be due to transient ATP (the chemical storage form of energy) depletion. This in turn leads to uric acid formation, which at excessively high levels acts as a pro-oxidant inside your cells.
According to an animal study published in 2016, long-term consumption of broccoli may reduce your chances of developing fatty liver and liver cancer caused by the standard American diet by lowering triglyceride levels in your liver.
How to Optimize Sulforaphane Content in Mature Broccoli
Ideally, broccoli should not be eaten raw. If you prefer raw food, you’d be better off eating raw broccoli sprouts instead of mature broccoli, as they’re a far more potent source of sulforaphane. Tests show three-day-old broccoli sprouts consistently contain up to 50 times the amount of anti-cancer compounds found in mature broccoli, including sulforaphane.
This super-charged nutrient-density means you can eat far less of them while still maximizing your benefits. If you’re partial to mature broccoli, you can maximize the sulforaphane content by preparing it properly, and combining it with specific foods. Eating broccoli raw will actually only give you about 12 percent of the total sulforaphane content theoretically available.
Research shows steaming mature broccoli spears for three to four minutes will increase the available sulforaphane content by eliminating epithiospecifier protein — a heat-sensitive sulfur-grabbing protein that inactivates sulforaphane — while still retaining the enzyme myrosinase, which converts glucoraphanin to sulforaphane. The latter is important because, without myrosinase, you cannot absorb the sulforaphane.
Do not steam the broccoli for more than five minutes, however, as beyond that point, you start losing valuable compounds. If you want to microwave your broccoli, be sure not to go past the 1-minute mark, as this will destroy a majority of the myrosinase needed for sulforaphane absorption. If you opt for boiling, blanch it in boiling water for no more than 20 to 30 seconds, then immerse it in cold water to stop the cooking process.
Also, be sure to use raw, freshly harvested broccoli whenever possible. Frozen broccoli has diminished ability to produce sulforaphane as myrosinase is quickly destroyed during the blanching process. Broccoli can also lose 80 percent of its glucoraphanin — the precursor of sulforaphane — in the first 10 days after harvest.
To increase sulforaphane content even further, eat it with a myrosinase-containing food such as mustard seed, daikon radishes, wasabi, arugula or coleslaw. A 2013 study that focused on mustard seed — which is said to contain a particularly resilient form of myrosinase — confirmed that mustard seed can boost sulforaphane formation even in boiled broccoli. Adding a myrosinase-rich food is particularly important if you eat the broccoli raw, or use frozen broccoli.
Article originally posted on mercola.com
Written By: Dr. Mercola
Cancer can be caused by tobacco smoke or by an inherited trait, but new research finds that most of the mutations that lead to cancer crop up naturally.
The authors of the study published Thursday poked a hornet’s nest by suggesting that many cancers are unavoidable.
The provocative findings by Bert Vogelstein and Cristian Tomasetti at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, have stirred up a heated scientific debate that started two years ago, when they published a report along similar lines.
Back then, critics said they were undercutting important messages about cancer prevention. So when these scientists had new results to report, Vogelstein addressed that concern head-on.
“We all agree that 40 percent of cancers are preventable,” he said at a news conference. “The question is, what about the other cancers that aren’t known to be preventable?”
Vogelstein, who is also an investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, explained how he and Tomasetti have refined that question. He notes that every time a perfectly normal cell divides, it makes several mistakes when it copies its DNA. These are naturally occurring mutations.
Most of the time, those mutations are in unimportant bits of DNA. That’s good luck. “But occasionally they occur in a cancer driver gene. That’s bad luck,” Vogelstein says.
After two or three of these driver genes get mutated in the same cell, they can transform that healthy cell into a cancer cell.
In their new paper in Science, the researchers set out to quantify how often those random errors are an inevitable part of cell division, how often they’re caused by nasty chemicals like tobacco smoke and how often they’re inherited.
The answer: 66 percent of the total mutations are random, about 29 percent are due to the environment and the remaining five percent are due to heredity.
These numbers vary depending on the type of cancer, they found.
Lung cancer is largely the result of environmental causes, while the vast majority of childhood cancer is a result of these bad-luck mutations, they found.
Vogelstein says parents often think they, somehow, are responsible for their child’s cancer, but that is not the case. “They need to understand that these cancers would have happened no matter what they did,” he says. “We don’t need to add guilt to an already tragic situation.”
Of course, people can reduce their risk of preventable cancer by avoiding tobacco, eating well and maintaining a healthy body weight. But the bad news is that most mutations arise naturally.
So, what can people do? “Nothing. Right now, nothing,” Vogelstein says.
But, he’s hopeful that if scientists focus on that question, they will have a more encouraging answer someday.Even without an action plan, the question of how much human cancer is caused by bad luck and how much is caused by bad things we do “is super fascinating,” says Martin Nowak, a biologist and mathematician at Harvard who wrote a commentary about the study for Science.
He says the findings are stirring up the field, and that’s a good thing.
“It’s very unclear to me about whether we have the tools to answer these questions,” he says. And, rather than settling the controversy raised by the scientists’ previous paper, “I think it will raise an even bigger controversy,” Nowak says.
One of the new sticking points is that mutations, while necessary for cancer to develop, aren’t the whole story. For example, some scientists say the study doesn’t fully account for how hormones can influence cancer.
Dr. Graham Colditz, an epidemiologist at Washington University in St. Louis isn’t convinced that hazards can been neatly sorted into the categories of hereditary, environmental and unavoidable mutations. “How these interplay with each other, I think is potentially more complex,” he says.
Vogelstein and Tomasetti agree on that point. The causes of cancer are complex.
“We’re not saying the only thing that determines the seriousness of the cancer, or its aggressiveness, or its likelihood to cause the patient’s death, are these mutations,” Vogelstein tells Shots. “We’re simply saying that they are necessary to get the cancer.”
This article originally appeared on NPR.org
Photo:Steve Gschmeissner/Science Source
Breast Cancer and chemotherapy took away her crownin’ glory. She promised God if she were to survive, she would enjoy every day of her life, ooh! On national television, Her diamond eyes are sparking. Bald-headed like a full moon shining, singing out to the whole wide world like, hey! India Arie co-wrote those lyrics to her song titled “I am not my hair.”
Some types of chemotherapy cause the hair on your head and other parts of your body to fall out. Radiation therapy can also cause hair loss on the part of the body that is being treated. Hair loss is called alopecia. However to the women who are afraid of losing or has lost their hair due to cancer treatment (my mother) and may feel less than beautiful, I’d like to share a few inexpensive ways on how to make your self feel beautiful and stylish in the process!!
- ROCK Colorful and Large Earrings-Not only will you stand out, but they will take away the attention you think is on your head. Charming Charlie is my go to place for trendy earrings.
- ROCK Sunglasses or Non-Prescription Eyewear-Ross, TJ. Maxx, Marshalls
- ROCK Wigs-You may want to discuss with your healthcare team about where to purchase one as some companies offers discount rates for cancer patients. Also, If you plan to buy a wig, get one while you still have hair so you can match it to the color of your hair.
- ROCK Scarves or Turbans-Charming Charlie, Wal-Mart, Target or any beauty supply store. You may also want to become creative by removing the scarf from your church or business suits.
- ROCK Hats-I wear them quite often. My go to stores are Belk and DSW. If you are not into the typical styles, feel free to customize them or even ROCK your organization or favorite sports team ball cap.
Once your hair starts to grow back, here are a few things you should consider:
- Be gentle.When your hair starts to grow back, you will want to be gentle with it. Avoid too much brushing, curling, and blow-drying. You may not want to wash your hair as frequently.
- After chemotherapy.Your hair often grows back in 2 to 3 months after treatment has ended. Your hair will be very fine when it starts to grow back. Sometimes your new hair can be curlier or straighter—or even a different color. In time, it may go back to how it was before treatment.
- After radiation therapy- Your hair often grows back in 3 to 6 months after treatment has ended. If you received a very high dose of radiation your hair may grow back thinner or not at all on the part of your body that received radiation.
I know some may think it’s easier said than done, but it really is how you choose to deal with the temporary loss. Once you embrace the new YOU, you may actually enjoy it! I HAVE!!
Photo:iStock
A rare form of eye cancer has struck a group of people in two locations in North Carolina and Alabama, confounding medical experts who are trying to determine whether the cases are linked.
Ocular melanoma typically affects 6 out of every 1 million people, but doctors have found dozens of cases where those affected have ties to either Huntersville, N.C., or Auburn, Ala. Many of those diagnosed attended Auburn University between 1983 and 2001 — at least three of them were friends.
At least 38 people who went to Auburn have reported being diagnosed with the disease, according to a Facebook page created by the patients. In Huntersville, at least 18 patients were identified in a formal investigation.
The Alabama Department of Health has declined to call the cases a cancer cluster yet, but researchers are investigating to determine whether there is a common cause for the diagnoses. A cluster is a higher-than-average number of cases identified in one particular geographic area over a limited period of time.
Unlike skin melanoma — which has been diagnosed more than 90,000 times this year — doctors typically see only 2,500 cases of ocular melanoma annually, says Dr. Marlana Orloff, an oncologist at the Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia, who is studying the cases. She says it is unlikely this group of patients got the cancer from sun or other UV light exposure.
“If it were something as simple as the sun or as simple as tanning bed use, we wouldn’t necessarily, I think, be seeing it in such restricted geographic locations,” Orloff tellsHere & Now‘s Robin Young.
Juleigh Green was the first person among at least 36 former Auburn students to be diagnosed with the disease in 1999. Two friends, Allison Allred and Ashley McCrary, were also treated for the cancer, and Green and Allred had to undergo eye removal surgery. The women told NBC’s Today show they were diagnosed just a few years after graduating from college.
“When I was diagnosed, I kept wanting to talk to someone who had been through this before and had done well,” Green told CNN. “But it seemed like nobody had heard of this or had any connection with anyone who had this, and that’s when I realized how incredibly rare it was.”
According to the Ocular Melanoma Foundation, the cancer develops from cells that produce the dark-colored pigment melanin. These cells are found in the skin, hair, eyes and lining of some internal organs.
The symptoms of ocular melanoma include dark spots on the eyes, flashes or blurry vision, Orloff says. Sometimes people have no symptoms at all, and the condition is identified during a routine eye exam.
The primary treatment — radiation therapy — is very effective, Orloff says. But in about half of patients, the cancer recurs, metastasizing or spreading to other parts of the body, most commonly in the liver.
“The most common site that we see the cancer turn up — most often within the first kind of three to five years — is in the liver, and once the disease metastasizes to the liver, there is no cure,” Orloff says.
The foundation notes that the exact cause of the melanoma is unknown, though it is most commonly found in people with lighter skin and blue eyes, with a median age of 55. A 2001 study in France found that people who worked as cooks or welders were at higher risk of getting the disease.
Orloff says what is remarkable about this group of cases is the relatively young ages of those diagnosed.
“One of the more unique things again about this [group] is that this is really young women,” she says. “In the Huntersville, N.C., group, two of the young girls who were … first diagnosed both went to the same high school, diagnosed in their 20s, died in their 30s, died at a young age.”
A research committee in Huntersville identified some toxic releases in the water and air, but nothing directly connected to the cancer, according to Charlotte-based WCNC-TV.
Allred, the Auburn student who was friends with Green, told CNN that she and at least two other patients lived in neighboring sorority houses and were all education majors. She also had to have her eye removed, but the cancer still spread to several other parts of her body, including her liver in 2008. She is still fighting the disease.
“We need the funding for the research to figure out what possibly could be the environmental cause,” she said. “There must be some link, and if we can find that link, we’re that much closer to finding a cure and preventing people from continuing to get this.”
Article written by Samantha Raphelson and appeared on npr.org
Image:Karen Bleier/AFP/Getty
When compared to the general population, it appears that people living with rheumatoid arthritis are at a greater risk for various types of cancer.
The findings from a variety of studies over the years found that the overall risk for cancer seems to be higher among people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) compared to people without the disease.
It’s worth noting that a greater risk for malignancy isn’t the only RA-cancer link. Some medications used to treat RA also bring on cancer, and vice versa.
According to the recent findings, people with RA were also actually less likely to have certain types of cancer. However, when they did get those forms of cancer, the symptoms were often worse.
Other cancer links
There have been other links noted between cancer and RA.
For people with both RA and squamous cell carcinoma, hematopoietic malignancies, or cancers of the upper aerodigestive tract and prostate, their outlook and mortality were both worse, according to a study published in December.
People who had RA along with prostate cancer had a 50 percent higher death rate than those who had prostate cancer but not RA.
The study also noted that people with RA have been shown to have an increased incidence of lung cancer with a worse outlook and a notably increased risk for lymphoproliferative malignancies, including Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
However, people who had both RA and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma had similar survival rates to people with this type of lymphoma from within the general population.
There’s some evidence that RA medications can cause an increased risk for cancer, even though some of the treatments for RA and cancer may occasionally overlap.
Some intravenous or injectable biologic drugs also warn of increased risks for certain cancers, such as lymphomas, when listing side effects. These drugs includes anti-TNF agents, JAK inhibitors, and B-cell inhibitors.
The challenge for medical professionals
This apparent risk between the therapies used to manage RA and potential increased malignancy could present a significant challenge to researchers and doctors.
People with RA have an increased risk for lymphoma and lung cancer, compared with the general population.
However, “this risk appears to be related to having RA itself, rather than with the use of biologic medications, as recent large studies have shown,” Dr. Laura Cappelli, MHS, assistant professor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Maryland, told Rheumatology Advisor.
Another rheumatologist, Dr. Eric L. Matteson, MPH, chair of rheumatology and professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic in Minnesota, told Rheumatology Advisor: “RA is associated with a greater than twofold increased risk for lymphoma. This risk is higher in patients with high disease activity and with more severe disease, including extra-articular involvement.”
Both doctors suggested that future research into the RA-cancer connection should focus on the disease mechanisms of RA that cause cancer to develop more frequently or more aggressively.
People who may be high-risk need to be identified, and the underlying biological mechanisms contributing to this correlation need to be investigated, they said.
Advice for patients
The Arthritis Foundation suggests that people with RA be mindful of whichever risk factors they’re able to control.
For example, quitting smoking is important, since RA and lung disease are linked at a higher prevalence and with a worse outlook and chance of death.
After all, it’s been found that people with RA who smoke are about 40 percent more likely to develop lung cancer than smokers who don’t have RA.
Researchers have noted that chronic inflammation may be a key component of an increased risk for cancer in people with RA.
The Arthritis Foundation’s website says that “an increased risk for a serious disease, even if it’s small, needs to be considered when deciding to take any medication.”
It later notes that uncontrolled RA can lead to serious and possibly dangerous health risks, too, so it’s important for people to weigh the risks and benefits when choosing a treatment plan to combat RA.
This article appeared on healthline.com
Image:Getty
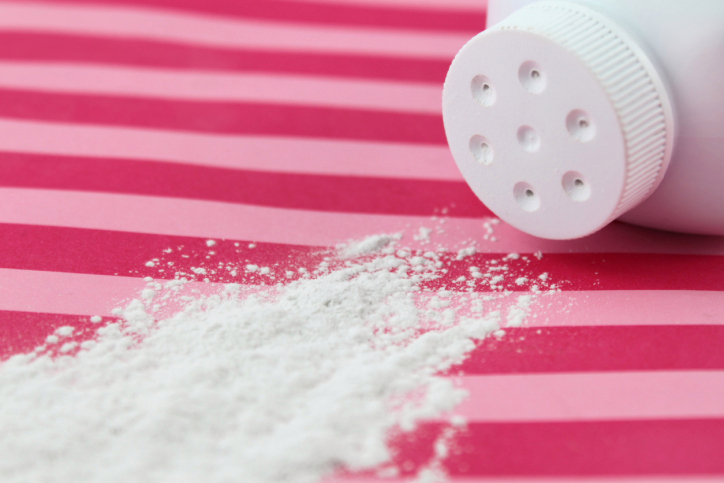
Johnson’s Baby Powder is a household favorite among babies and adults, but recent news has women revisiting horrific claims that are far from brand new. A Missouri jury recently awarded $72 million in damages to the family of Jackie Fox, an Alabama woman who died at age 62 of ovarian cancer in October 2015. Fox’s family believes the cancer was caused by her regular use of the popular Johnson & Johnson brand powder and other products containing talcum.
“It just became second nature, like brushing your teeth,” said Fox’s son, Marvin Salter, of his mother’s use and trust of the product. “It’s a household name.”
READ: Silent Killer: What Black Women Must Know About Ovarian Cancer
Johnson & Johnson was found guilty of negligence in a 10-2 jury vote for failure to warn consumers about potential risks of its products.
According to the American Cancer Society, approximately 22,000 women will be diagnosed with ovarian cancer this year, with about 14,000 likely to die this year from it.
Among the many risk factors for ovarian cancer, the American Cancer Society also lists talcum powder:
It has been suggested that talcum powder applied directly to the genital area or on sanitary napkins may be carcinogenic (cancer-causing) to the ovaries. Some, studies suggest a very slight increase in risk of ovarian cancer in women who used talc on the genital area. In the past, talcum powder was sometimes contaminated with asbestos, a known cancer-causing mineral. This might explain the association with ovarian cancer in some studies. Since the 1970s, however, body and face powder products have been required by law to be asbestos-free. Proving the safety of these newer products will require follow-up studies of women who have used them for many years. There is no evidence at present linking cornstarch powders with any female cancers.
What Is Talc?
It is estimated that up to 40% of women today may use talc at least occasionally. Talc is a naturally occurring mineral made of magnesium, silicon, oxygen and hydrogen. It is commonly used in cosmetics and personal care products – like talcum powder (“baby powder”) – to absorb moisture, which is what many people also use the product for to keep skin dry and prevent rashes.
READ: The 6 Types of Ovarian Cysts
A possible link between talcum powder and cancer has been suspected since the early 1970s. British researchers found talc particles “deeply embedded” in 10 of the 13 ovarian tumors they studied.
The investigative watchdog group FairWarning, reported:
In 1982, the journal Cancer published the first study showing a statistical link between genital talc use and ovarian cancer. The lead author, Dr. Daniel Cramer, a gynecologist and Harvard Medical School professor, recently co-authored a new study that found a 33 percent higher rate of ovarian cancer among women who used talc for feminine hygiene.
The highest risk was for women who used talc powder the longest. Altogether, about 20 epidemiological studies have found increased rates of ovarian cancer risk for women who reported using talc for hygiene purposes, though other studies have found no association.
In an interview with FairWarning, Fox’s son, Marvin Salter, said, “Obviously, the final outcome is something that my mother wanted.” He said, “It really wasn’t about the damages that were awarded,” but creating “awareness around this issue that has been suppressed for so many years by Johnson & Johnson.”
Proper Vaginal Care
Although there may not be any studies to date that prove a causal relationship between talcum powder and ovarian cancer, where there is smoke there is likely fire. The vagina does not require harsh chemicals to remain so fresh and so clean. Many health professional advise against douching, as well as perfumed soaps and powders. Improving your diet can also have a positive effect on your vaginal health.
Originally Posted on Blackdoctors.org